INTRODUCTION TO YOGA
Yoga is a very important spiritual discipline based inner science of body. It is an extremely subtle science which produce harmony between mind and body.
It is an art as well as scince of healthy living style. Word ‘Yoga’ is derived from the Sanskrit word ‘Yuj’, which means ‘to join’ or ‘to yoke’ or ‘to unite’.
According to the Yogic scriptures the practice of Yoga leads to the union of individual consciousness with Universal Consciousness.
It indicates a perfect harmony between Man & Nature as well as the mind and body. According to the scientists everything in the universe is a forms of similir power i.e every living thing is a part of a supreme power.
One who agreed and experiences this existence, said in yoga and he is called as a yogi.
योग शरीर का आंतरिक विज्ञान पर आधारित एक बहुत ही महत्वपूर्ण आध्यात्मिक अनुशासन है। यह एक अत्यंत सूक्ष्म विज्ञान है जो मन और शरीर के बीच सामंजस्य स्थापित करता है।
यह एक कला के साथ-साथ स्वस्थ जीवन शैली का विज्ञान भी है। 'योग' शब्द संस्कृत के 'युज' शब्द से बना है, जिसका अर्थ है 'जुड़ना' या 'जुड़ना' या 'एकजुट होना'।
योग शास्त्रों के अनुसार योग के अभ्यास से व्यक्तिगत चेतना का सार्वभौमिक चेतना के साथ मिलन होता है।
यह मनुष्य और प्रकृति के साथ-साथ मन और शरीर के बीच एक पूर्ण सामंजस्य का संकेत देता है। वैज्ञानिकों के अनुसार ब्रह्मांड में सब कुछ समान शक्ति का एक रूप है यानी हर जीव एक सर्वोच्च शक्ति का हिस्सा है।
जिसने इस अस्तित्व को स्वीकार किया और अनुभव किया, उसने योग में कहा और उसे योगी कहा जाता है।
The aim of Yoga is Self-realization, to overcome all kinds of sufferings leading to 'the state of liberation' or ‘freedom’ (Kaivalya).
Living with freedom in all path of life health and harmony.The main objectives of Yoga practice is to create self control physically and mentally.
"Yoga” is also refers to an inner science comprising with variety of methods by which human beings can realize the inner unity and achieve mastery
over their destiny. Yoga is widely considered as an ‘immortal cultural outcome’ of Indus Saraswati Valley civilization – dating back to 2700 B.C.,
has proved. It is a upliftmeny of humanity in both way materialistic and spiritual.
योग का उद्देश्य आत्म-साक्षात्कार है, 'मुक्ति की स्थिति' या 'स्वतंत्रता' (कैवल्य) की ओर ले जाने वाले सभी प्रकार के कष्टों को दूर करना।
जीवन के सभी पथों में स्वास्थ्य और सद्भाव के साथ स्वतंत्रता के साथ रहना। योग अभ्यास का मुख्य उद्देश्य शारीरिक और मानसिक रूप से आत्म-नियंत्रण बनाना है।
"योग" एक आंतरिक विज्ञान को भी संदर्भित करता है जिसमें विभिन्न प्रकार की विधियां शामिल हैं जिनके द्वारा मनुष्य आंतरिक एकता का एहसास कर सकता है और महारत हासिल कर सकता है
उनके भाग्य के ऊपर। योग को व्यापक रूप से सिंधु सरस्वती घाटी सभ्यता के 'अमर सांस्कृतिक परिणाम' के रूप में माना जाता है - 2700 ई.पू.
सिद्ध कर दिया है। यह भौतिकवादी और आध्यात्मिक दोनों तरह से मानवता का उत्थान है।
A Brief History and Development of Yoga
The practice of Yoga is believed to have started with the very dawn of civilization.
The science of yoga has its origin thousands of years ago, long before the first religions or belief systems were born.
In the yogic lore, Shiva is seen as the first yogi or Adiyogi, and the first Guru or Adi Guru.
Historical evidences of the existence of Yoga were seen in these periods classified as
माना जाता है कि योग का अभ्यास सभ्यता की शुरुआत के साथ शुरू हुआ था।
योग के विज्ञान की उत्पत्ति हजारों साल पहले हुई थी, पहले धर्मों या विश्वास प्रणालियों के जन्म से बहुत पहले।
योग विद्या में, शिव को पहले योगी या आदियोगी और पहले गुरु या आदि गुरु के रूप में देखा जाता है।
योग के अस्तित्व के ऐतिहासिक प्रमाणों को इन कालखंडों में वर्गीकृत किया गया है:
The pre-Vedic period (2700 B.C.)
This period is considered till Patanjali’s period.The main sources, from which we get the information about Yoga practices and the related literature during this period, are available in Vedas (4), Upanishads(108), Smritis, teachings of Buddhism, Jainism, Panini, Epics (2), Puranas (18) etc.
यह काल पतंजलि के काल तक माना जाता है। मुख्य स्रोत, जिनसे हमें योगाभ्यास और उससे संबंधित जानकारी प्राप्त होती है। इस अवधि के दौरान साहित्य, वेद (4), उपनिषद (108), स्मृति, बौद्ध धर्म, जैन धर्म, पाणिनी, महाकाव्य (2), पुराण (18) आदि की शिक्षाओं में उपलब्ध हैं।
Period between 500 BC - 800 A.D.
This period is considered as the Classical period which is also considered as the most fertile and prominent period in the history and development of Yoga. This period can be mainly dedicated to two great religious teachers of India –Mahavir and Buddha. The concept of Five great vows – Pancha mahavrata- by Mahavir and Ashta Magga or eightfold path by Buddha - can be well considered as early nature of Yoga sadhana. We find its more explicit explanation in Bhagawadgita which has elaborately presented the concept of Gyan yoga, Bhakti yoga and Karma Yoga. Patanjali’s yoga sutra besides containing various aspects of yoga, is mainly identified with eight fold path of Yoga. The very important commentary on Yoga sutra by Vyasa was also written.
इस अवधि को शास्त्रीय काल माना जाता है जिसे योग के इतिहास और विकास में सबसे उपजाऊ और प्रमुख अवधि भी माना जाता है। यह अवधि मुख्य रूप से भारत के दो महान धार्मिक शिक्षकों-महावीर और बुद्ध को समर्पित हो सकती है। पंच महाव्रत- महावीर द्वारा और अष्ट मग्गा या बुद्ध द्वारा अष्टांग मार्ग - की अवधारणा को योग साधना की प्रारंभिक प्रकृति के रूप में अच्छी तरह से माना जा सकता है। हम भगवद्गीता में इसकी अधिक स्पष्ट व्याख्या पाते हैं जिसने ज्ञान योग, भक्ति योग और कर्म योग की अवधारणा को विस्तृत रूप से प्रस्तुत किया है। पतंजलि के योग सूत्र में योग के विभिन्न पहलुओं को समाहित करने के अलावा, मुख्य रूप से योग के अष्टांगिक मार्ग से पहचाना जाता है। व्यास द्वारा योग सूत्र पर अत्यंत महत्वपूर्ण भाष्य भी लिखा गया था।
Period between 800 A.D. - 1700 A.D.
This period is recognized as the Post Classical period wherein the teachings of great Acharyatrayas-Adi Shankracharya, Ramanujacharya, Madhavacharya-were prominent during this period. The teachings of Suradasa, Tulasidasa, Purandardasa, Mirabai were the great contributors during this period.
इस अवधि को उत्तर शास्त्रीय काल के रूप में मान्यता प्राप्त है, जिसमें महान आचार्यों-आदि शंकराचार्य, रामानुजाचार्य, माधवाचार्य-की शिक्षाएं इस अवधि के दौरान प्रमुख थीं। इस अवधि के दौरान सूरदास, तुलसीदास, पुरंदरदास, मीराबाई की शिक्षाओं का महान योगदान था।
The period between 1700 - 1900 A.D.
This period is considered as Modern period in which the great Yogacharyas- Ramana Maharshi, Ramakrishna Paramhansa, Paramhansa Yogananda, Vivekananda etc. have contributed for the development of Raja Yoga.
इस काल को आधुनिक काल के रूप में माना जाता है जिसमें महान योगाचार्यों- रमण महर्षि, रामकृष्ण परमहंस, परमहंस योगानंद, विवेकानंद आदि ने राज योग के विकास में योगदान दिया है।
Do and Do'nt for Yoga Practitioners
DO'S
- Keep clean of surroundings, body and mind.
- Should be practiced on an empty stomach can be small amount of honey in lukewarm water.
- Bladder and bowels should be empty before starting Yogic practices.
- Practice sessions should start with a prayer to relax the mind.
- practices shall be start slowly in a relaxed manner with awareness of the body and breath.
- A Warm up exercise and stretches before asanas is mandatory to avoid injuries.
- Stay hydrated before going into yoga practice.
- Wear supportive, Light and comfortable cotton clothes.
- Practice in a well ventilated room with a pleasant flow of fresh air.
- Use a mat with a good grip.
- Complete the yoga session with relaxation techniques.
- Do not hold the body tight or give undue jerks to the body.
- Relax for 10 seconds at least after each yoga exercise.
- Yoga session should end with meditation or deep silence.
- should not be performed in a state of exhaustion, illness, in a hurry
- Women should perform yoga practice especial asanas during their menses or pregnancy instead of all regular yoga. Avoid is best deal during menstruation and pregnancy days.
- Don’t perform yoga immediately after meals.
- Don’t shower or drink water or eat food for 30 minutes after doing yoga.
- During illness, surgeries, or any sprains or fractures, one can resume yoga after consulting experts.
- Don’t do strenuous exercises after yoga.
- Do not practice yoga on naked ground.
- Don’t practice yoga in adverse and extreme weather conditions
Benefits of Regular Yoga
Medical research has uncovered many physical and mental benefits that Yoga offers, corroborating the experiences of millions of practitioners, some of them are as:
- To improve physical fitness, musculoskeletal functioning and cardio-vascular health.
- To control over diabetes, Obesity, respiratory disorders, hypertension, hypotension and many lifestyle- related disorders.
- To reduce depression, fatigue, anxiety disorders and stress.
- To regulate menopausal symptoms in women.
- To creaate self realisation, Peace in mind and self satisfaction.
General Perceptions About Yoga
- Yoga has no age limitation, can perform at any age.
- Yoga sessions can be schedule at any time of the day.
- To practice Yoga in a quiet and properly ventilated room or out door near trees.
- Wear loose, light and comfortable clothes
- Remove your spectacles, watches or any jewellery before starting yoga.
- Prefer Yoga mats or blanket for yoga.
- Eat natural food filled with nutrients.
- Consciousness is a basic Yoga rule to follow.
- The body must be in relax during the practice.
- Do not exert any sort of force on the body while practicing.
- Yoga should never be practiced after sun-bath
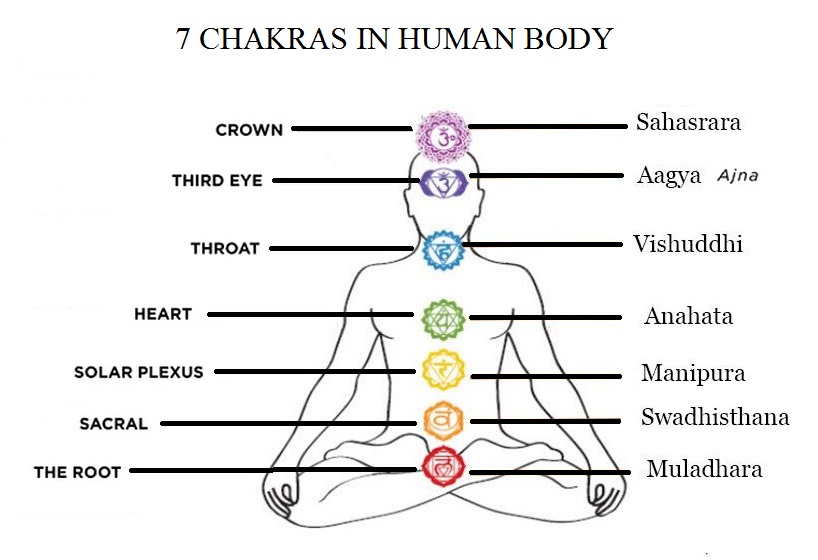
Chakras in Human Body
There are many controlling points in our body as shown figure from which the rulling over the human can be controlled: